Laser Hardening
In modern manufacturing, component failure rarely begins at the core – it starts at the surface.
Component wear, fatigue and surface degradation are the primary reasons why critical parts
fail prematurely. This is where laser hardening technology is redefining surface treatment
by delivering strength exactly where it is needed, without compromising dimensional
accuracy.
Laser hardening is rapidly emerging as the preferred solution for industries that demand durability, precision and repeatable quality.

The Goal of Introducing Laser Hardening
The objective of laser hardening is simple yet powerful:
To increase surface hardness and wear resistance while preserving the original core properties of the component.
By applying controlled, localized heat only to critical zones, laser hardening helps industries
achieve:
- Longer component life
- Higher resistance to wear and fatigue
- Minimal distortion
- Faster processing compared to conventional heat treatment
- Consistent, repeatable results suitable for automation
This makes laser hardening ideal for high-load and high-precision applications where
traditional methods often fall short.
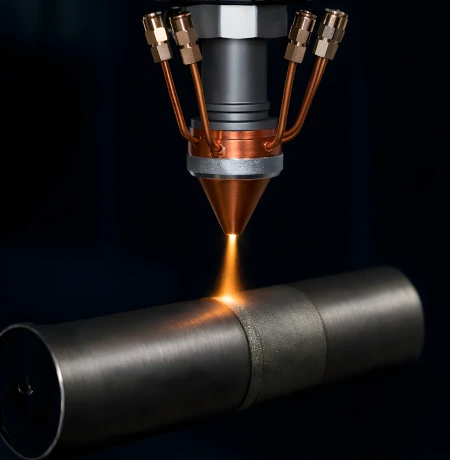
What Is Laser Hardening?
Laser hardening is an advanced surface heat-treatment process in which a focused laser beam
rapidly heats the surface layer of a metal component. Once the laser moves away, the heat
dissipates naturally into the bulk material, causing self-quenching. This rapid heating and
cooling transforms the surface into a martensitic hardened layer, while the core remains
unchanged.
Key Characteristics of Laser Hardening
- Typical hardening depth: 0.5 to 2.5 mm
- No external quenching media required
- Clean, controlled and highly repeatable process
- Suitable for carbon steels, alloy steels, tool steels and automotive-grade steels
Why Laser Hardening Is the Preferred Choice?
Localized Heating for Precision
Laser Hardening heats up only the required surface area which needs to be hardened. This
protects adjacent features and ensures dimensional stability – critical for precision
components.
Extremely Low Distortion
Compared to flame or induction hardening, laser hardening produces negligible warpage,
reducing or eliminating post-processing and straightening.
High Surface Hardness
Laser-hardened surfaces achieve excellent hardness levels:
- 42CrMo: up to HRC 55–60+
- Tool steels: up to HRC 58–62+
Automation and Repeatability
The process is easily automated, making it ideal for batch production with consistent quality
across parts.
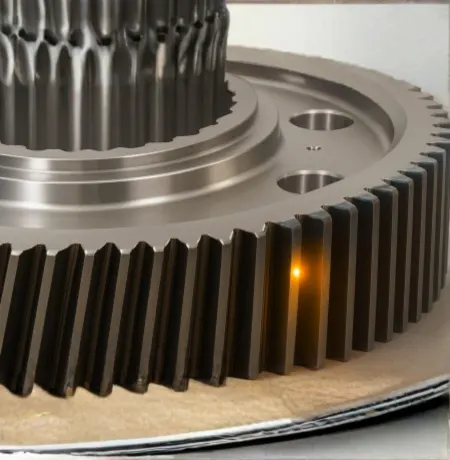
Applications Supported by Laser Hardening
Laser hardening is widely used in applications where surfaces are exposed to friction, impact,
or cyclic loading.

Gears and Power Transmission
- Spur and helical gears
- Gear teeth strengthening and repair
- Splines and couplings

Automotive Components
- Shafts and axles
- Cam followers and rocker arms
- Crank journals

Industrial Machinery
- Rollers and guide rails
- Wear plates and sliding surfaces

Tooling and Dies
- Punches and moulds
- Cutting edges
- Shear blades
These applications benefit from improved wear resistance while maintaining tight tolerances
and structural integrity.
Why Laser Hardening Makes Sense Today
As industries move toward lighter designs, tighter tolerances, traditional heat-treatment
methods struggle to keep up. Laser hardening offers a modern alternative which is much
cleaner, precise and efficient.
It is particularly effective where:
- Controlled hardness is critical
- Distortion cannot be tolerated
- Only selective areas require strengthening
With laser hardening technology, Light Mechanics is preparing to deliver reliable, high-performance surface treatment solutions for automotive, tooling, industrial machinery and
heavy engineering applications.
Laser hardening is not just about making parts harder – it’s about making them last longer,
perform better and stay accurate with tight tolerances.